Basic Collision Response
A faith that cannot survive collision with the truth is not worth many regrets.
— Arthur C. Clarke, The Exploration of Space
Simple Bounce Physics
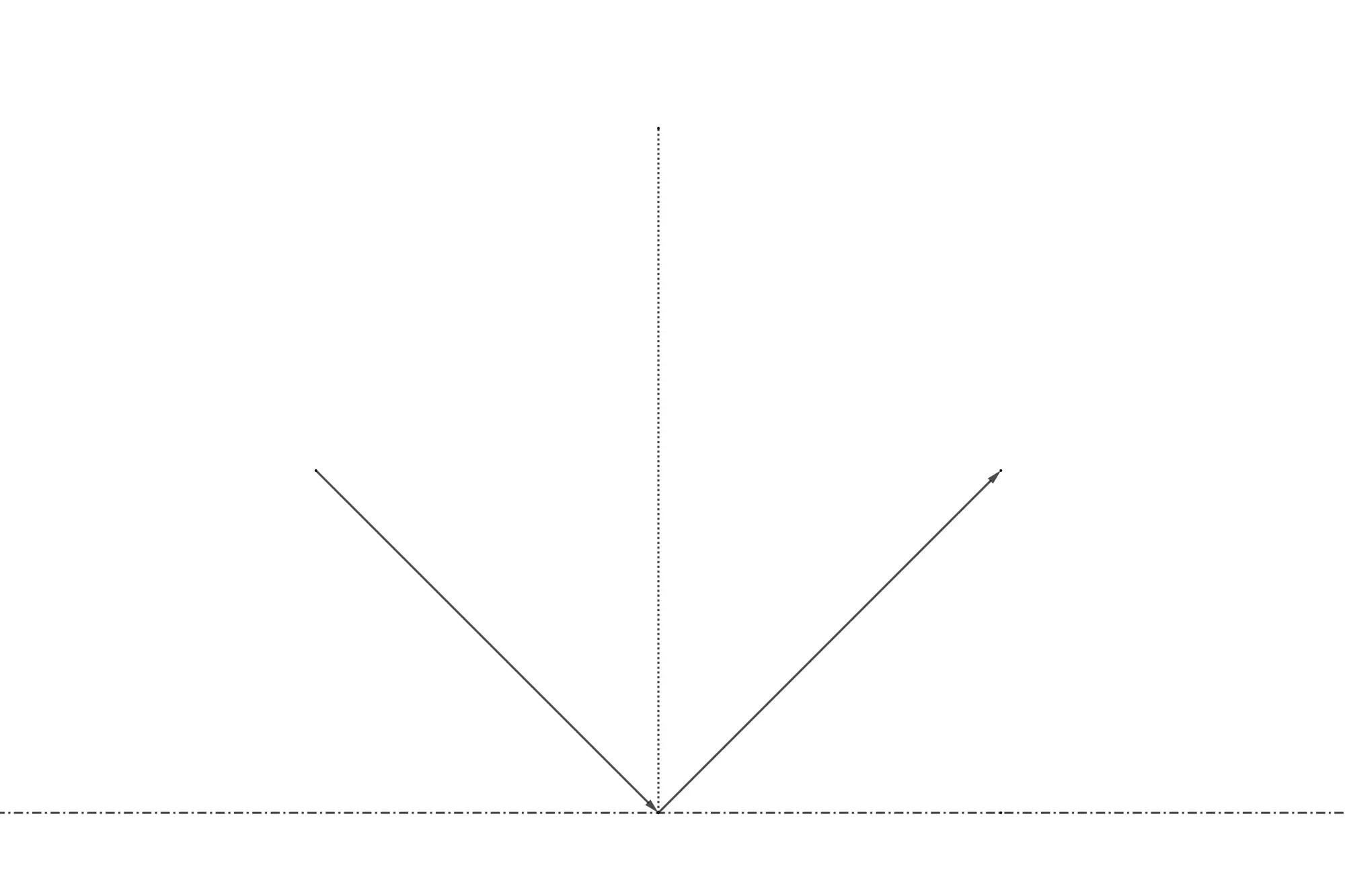
A previous tutorial showcased a Kicker-table with a ball bouncing off its edges. This behaviour is easily
simulated by observing that the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence. When the ball hits one of the sides
of the table, then it always reflects off the side at an angle equal and opposite to its initial trajectory.
 Here is the C++-code of that demo:
Here is the C++-code of that demo:
void Ball::collision(){ // compute new starting velocity velocity->x = initialVelocity * std::cosf(angle); velocity->y = initialVelocity * std::sinf(angle);
// adjust sign of the acceleration acceleration->x = std::copysignf(acceleration->x, -velocity->x); acceleration->y = std::copysignf(acceleration->y, -velocity->y);}
util::Expected<void> PlayState::update(const double deltaTime){ if (isPaused) return { };
// update the ball and table ball->update(deltaTime, table->frictionCoeffK);
// check boundaries if (ball->position->x < table->leftX + ball->radius) { ball->position->x = table->leftX + ball->radius; ball->initialVelocity = ball->velocity->getLength(); ball->angle = (float)(M_PI - ball->angle); ball->collision(); } if (ball->position->x > table->rightX - ball->radius) { ball->position->x = table->rightX - ball->radius; ball->initialVelocity = ball->velocity->getLength(); ball->angle = (float)(M_PI - ball->angle); ball->collision(); } if (ball->position->y < table->leftY + ball->radius) { ball->position->y = table->leftY + ball->radius; ball->initialVelocity = ball->velocity->getLength(); ball->angle = (float)(2*M_PI - ball->angle); ball->collision(); } if (ball->position->y > table->rightY - ball->radius) { ball->position->y = table->rightY - ball->radius; ball->initialVelocity = ball->velocity->getLength(); ball->angle = (float)(2*M_PI - ball->angle); ball->collision(); }
...}This seems to be a bit too complicated — there is no way I want to think about angles each time I want an object to bounce from a surface. In the following, we will derive a much easier formula by using simple geometry and a mathematical technique called projection.
Planes of any Orientation
This tutorial tries to give a better explanation to the above phenomenon by deriving the equations of reflection from any hypersurface, i.e. off a line in 2D and off a plane in 3D. Once again, we observe that the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence relative to the normal vector of the plane:
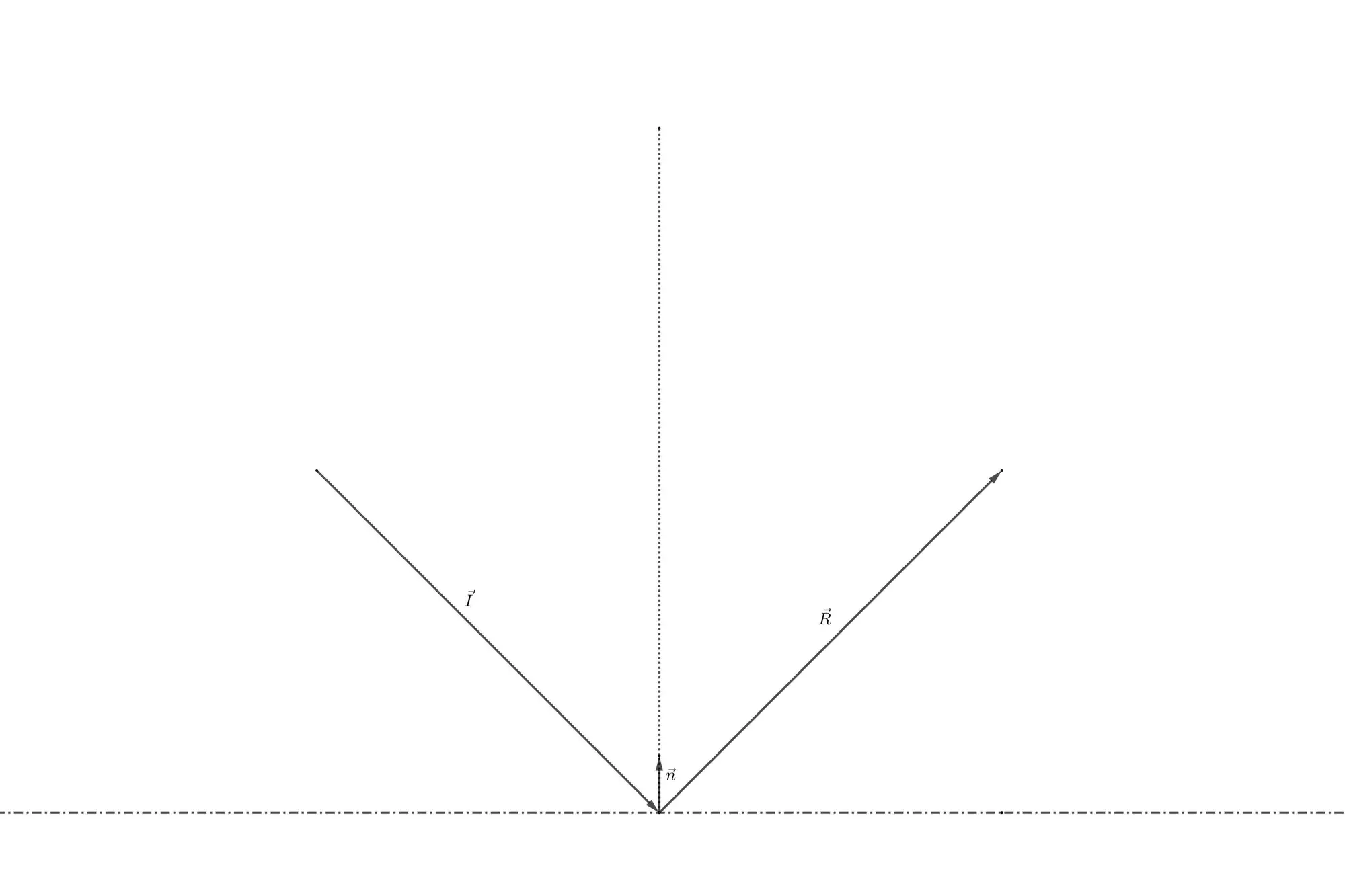 If you forgot what the normal vector of a plane is, check out this tutorial.
If you forgot what the normal vector of a plane is, check out this tutorial.
In the 2D case, basically speaking, the normal vector of a line can be found by using the scalar product
Projections
Now, how does the normal vector help to find the vector of reflection? First, the projection of the vector of incidence along the normal vector must be computed (think of the shadow cast by shining a light from the left of the above figure). The following figure shows the projection of a point to a vector space:
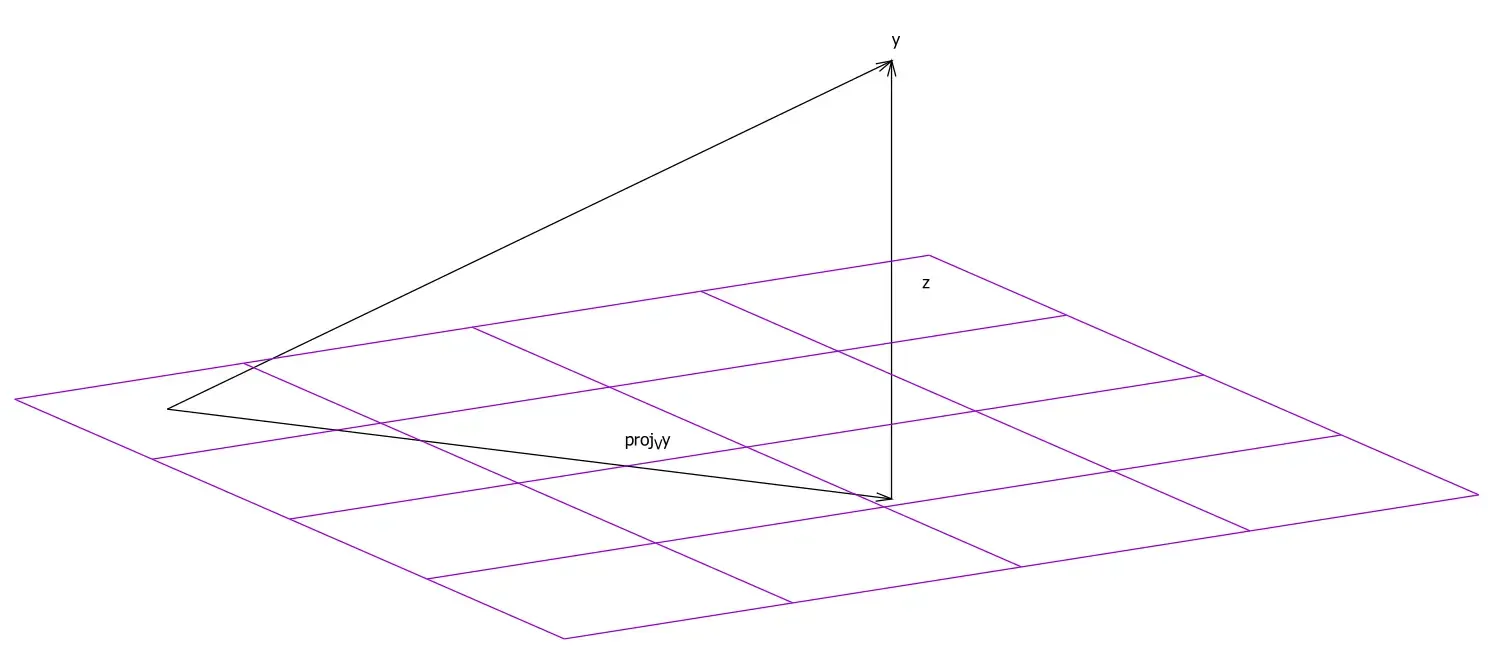
A projection on a vector space
Thus, in our 2D-example, the projection of the vector
Finding the Vector of Reflection
Now finding the vector of reflection,
An Example
As an example, let us compute the reflection vector when the vector of incidence is given by
Implementation
The function to compute the vector of reflection is straightforward, we simply use the above formula to change the vector of incidence to become the vector of reflection:
namespace mathematics{ float scalarProduct2F(Vector2F x, Vector2F y) { // standard scalar product return x.x * y.x + x.y * y.y; }
...
void reflectionVector(Vector2F* incidence, Vector2F normal) { // compute projection: b(-I,n)n float coef = -2 * scalarProduct2F(*incidence, normal);
// return the vector of reflection: r = -2b(I,n)n+I *incidence += normal * coef; }
...}With this function, it is now possible to greatly simplify the above code to handle the collision of the ball with the walls of the Kicker-table:
util::Expected<void> PlayState::update(const double deltaTime){ if (isPaused) return { };
// update the ball and table ball->update(deltaTime, table->frictionCoeffK);
// check boundaries if (ball->position->x < table->leftX + ball->radius) // left wall mathematics::reflectionVector(ball->velocity, table->normalLeft); if (ball->position->x > table->rightX - ball->radius) // right wall mathematics::reflectionVector(ball->velocity, table->normalRight); if (ball->position->y < table->leftY + ball->radius) // top wall mathematics::reflectionVector(ball->velocity, table->normalTop); if (ball->position->y > table->rightY - ball->radius) // bottom wall mathematics::reflectionVector(ball->velocity, table->normalBottom);
...}As you can see, it is no longer necessary to think about angles and Pi or whatever, all that needs to be done is to define a normal vector for each wall and the rest is just mathemagical. (I have always wanted to make that joke!)
In the next tutorial, we will learn how to improve the above collision detection code.
References
- Geogebra
- Tricks of the Windows Programming Gurus, by A. LaMothe
- Wikipedia